ENT stands for ear, nose, and throat, which is a medical specialty that deals with the diagnosis, management, and treatment of disorders related to the ears, nose, and throat. An otolaryngologist, also known as an ENT specialist in Chennai, is a medical doctor who is trained to diagnose and treat various conditions affecting these organs, which are all connected and have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life.
Otolaryngologists undergo several years of residency training after medical school to become experts in the medical and surgical treatment of the ear, nose, and throat. They use various diagnostic tools and treatment options, including antibiotics, antihistamines, surgery, hearing aids, and speech therapy, to manage these conditions.
ENT Specialist in Chennai
Our Doctors
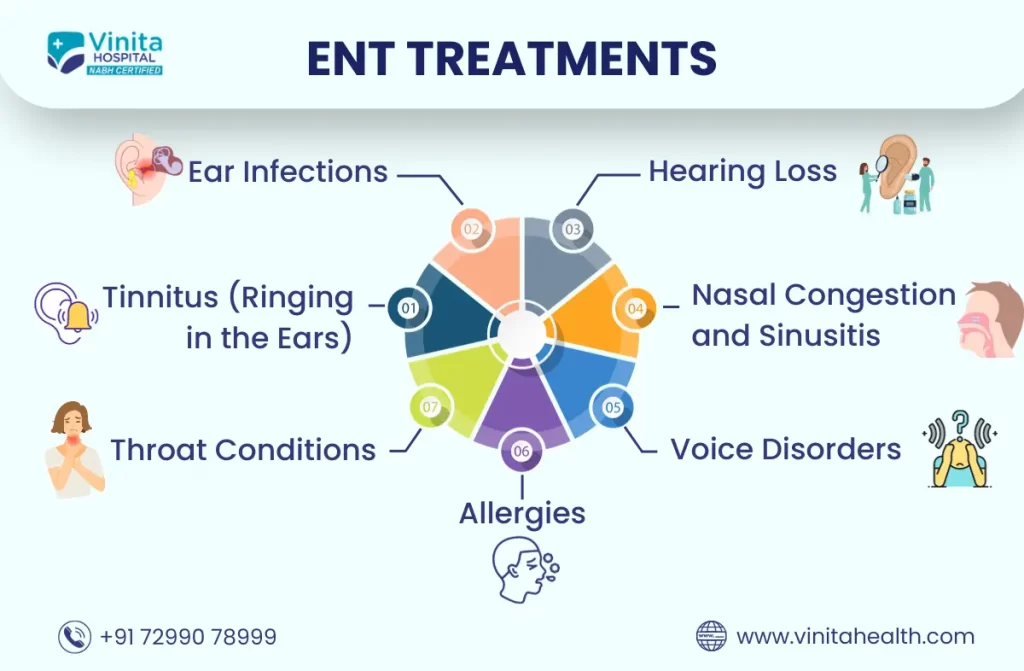
Some of the common ENT conditions are
- Ear infections: Ear infections can cause pain, fluid discharge, and temporary hearing loss. They are common in children but can occur at any age.
- Hearing loss: Hearing loss can occur due to aging, exposure to loud noise, infections, or genetic factors. ENT specialist in Chennai can evaluate and manage hearing loss using various treatment options.
- Tinnitus: Tinnitus is a ringing or buzzing in the ears that can be caused by a variety of factors, including exposure to loud noise, ear infections, or certain medications.
- Vertigo: Vertigo is a feeling of dizziness or spinning that can be caused by problems in the inner ear, such as benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), vestibular neuritis, or Meniere’s disease.
- Sinusitis: Sinusitis is an inflammation of the sinuses, which can cause nasal congestion, headache, facial pain, and fever. It can be caused by infections, allergies, or structural abnormalities.
- Allergies: Allergies can cause nasal congestion, runny nose, sneezing, and itching. ENT specialist in Chennai can identify the specific substances that trigger allergies and manage them with medications or immunotherapy.
- Nasal polyps: Nasal polyps are growths that develop in the nasal cavity and can cause nasal congestion, runny nose, and a loss of sense of smell. They can be treated with medications or surgery.
- Deviated septum: A deviated septum is a condition where the nasal septum, the cartilage that separates the nostrils, is crooked or displaced. It can cause nasal congestion, snoring, and breathing difficulties and can be corrected with surgery.
- Throat infections: Throat infections, such as tonsillitis or pharyngitis, can cause sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and fever.
- Swallowing disorders: Swallowing disorders, such as dysphagia, can make it difficult to swallow food or liquid, and can be caused by a variety of factors including neurological disorders, structural abnormalities, or cancer
The symptoms of ENT (ear, nose, and throat) disorders can vary depending on the specific condition, but some common symptoms may include:
- Ear pain or discomfort
- Hearing loss or ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Dizziness or vertigo
- Nasal congestion or runny nose
- Sinus pressure or headache
- Sore throat or difficulty swallowing
- Hoarseness or changes in voice
- Cough
- Difficulty breathing
- Fatigue or weakness
In addition to these general symptoms, specific ENT disorders may have their own unique symptoms. For example, a deviated septum may cause snoring or sleep apnea, while allergies may cause itchy or watery eyes. If you experience any of these symptoms or other concerning changes related to your ears, nose, or throat, it’s important to see an ENT specialist in Chennai for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis of ENT conditions
ENT (ear, nose, and throat) conditions can be diagnosed through various methods, including:
- Medical history and physical exam: The ENT specialist in Chennai will review your medical history, ask about your symptoms, and perform a physical examination of your ears, nose, and throat.
- Hearing tests: Hearing tests, such as audiometry or tympanometry, may be conducted to evaluate hearing loss and other ear-related issues.
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans, may be performed to evaluate structural abnormalities or injuries to the head and neck.
- Endoscopy: An endoscope, a thin tube with a camera and light, may be inserted into the nose or throat to examine the internal structures.
- Allergy testing: If allergies are suspected, skin tests or blood tests may be performed to identify the specific allergens that trigger the symptoms.
- Biopsy: A small tissue sample may be taken from a suspicious growth or lesion in the ear, nose, or throat to determine if it is cancerous or non-cancerous.
- Balance tests: Balance tests, such as the Dix-Hallpike maneuver or caloric testing, may be used to evaluate dizziness or vertigo.
Once a diagnosis is made, the ENT specialist in Chennai will develop a treatment plan that may include medications, surgery, hearing aids, or other therapies based on the specific condition and its severity.
ENT (ear, nose, and throat) conditions can be treated in various ways depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some common treatments for ENT conditions include:
Medications: Many ENT conditions can be treated with medications, such as antibiotics for ear infections, nasal sprays or antihistamines for allergies, or steroids to reduce inflammation in the sinuses or throat.
Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be required to treat ENT conditions. For example, surgery may be needed to remove tonsils or adenoids in cases of chronic tonsillitis or to correct a deviated septum that causes breathing difficulties.
ENT (ear, nose, and throat) surgeries can be performed to treat a variety of conditions, including:
- Tonsillectomy: A tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the tonsils, which may be necessary in cases of recurrent tonsillitis, sleep apnea, or other conditions affecting the tonsils.
- Adenoidectomy: An adenoidectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the adenoids, which are located in the back of the nose and may become enlarged or infected, causing breathing difficulties or ear infections.
- Sinus surgery: Sinus surgery may be performed to treat chronic sinusitis, nasal polyps, or other conditions affecting the sinuses, by opening up blocked sinuses or removing polyps.
- Ear tube insertion: Ear tube insertion is a common surgical procedure to treat chronic ear infections, where a small tube is inserted into the eardrum to help drain fluids and reduce the risk of future infections.
- Septoplasty: Septoplasty is a surgical procedure to correct a deviated septum, which can cause breathing difficulties or snoring.
- Thyroidectomy: A thyroidectomy is a surgical procedure to remove all or part of the thyroid gland, which may be necessary in cases of thyroid cancer, goiter, or other thyroid conditions.
- Cochlear implantation: Cochlear implantation is a surgical procedure to treat severe hearing loss, where a small electronic device is implanted in the ear to stimulate the auditory nerve and improve hearing.
Hearing aids: Hearing aids may be recommended for individuals with hearing loss to improve their hearing and communication abilities.
Allergy immunotherapy: Allergy immunotherapy, such as allergy shots, may be recommended for individuals with severe allergies to help desensitize them to specific allergens and reduce their symptoms.
Voice therapy: Voice therapy may be recommended for individuals with vocal cord disorders, such as nodules or polyps, to improve their voice quality and reduce strain on the vocal cords.
Lifestyle changes: Making lifestyle changes, such as avoiding triggers that worsen symptoms, quitting smoking, or using a humidifier, may help manage some ENT conditions. It’s important to seek medical advice from an ENT specialist in Chennai to determine the best course of treatment for your specific condition.
Treatment for Swallowing Disorders
Treatment for swallowing disorders, also known as dysphagia, will depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some common treatments for swallowing disorders include:
- Diet modifications: Individuals with swallowing disorders may need to make dietary modifications, such as avoiding certain foods or altering the texture of food, to make it easier to swallow.
- Swallowing exercises: Swallowing exercises, such as tongue strengthening exercises or exercises that focus on improving the coordination of swallowing muscles, may be recommended by a speech-language pathologist to improve swallowing function.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as muscle relaxants or medications that reduce acid reflux, may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of dysphagia.
- Surgical interventions: In some cases, surgical interventions may be needed to treat the underlying cause of the swallowing disorder, such as removing an obstruction or repairing a structural abnormality.
- Feeding tubes: In severe cases of dysphagia, a feeding tube may be necessary to ensure adequate nutrition.
- Lifestyle modifications: Individuals with dysphagia may benefit from lifestyle modifications such as avoiding alcohol, avoiding lying down for at least an hour after eating, and eating smaller, more frequent meals.
Lifestyle modifications can be an important part of managing ENT (ear, nose, and throat) conditions, and may be recommended by an ENT specialist in Chennai in addition to medical treatments. Here are some common lifestyle modifications that may be suggested for ENT patients:
Avoiding allergens: For patients with allergies, avoiding allergens that trigger symptoms can help to reduce inflammation and improve overall health. This may involve avoiding specific foods, environmental triggers, or other allergens.
Maintaining good hygiene: Proper hygiene can help to prevent the spread of infections and reduce the risk of developing ENT conditions. This may include frequent hand washing, regularly cleaning surfaces, and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick.
Managing stress: Stress can contribute to a number of ENT conditions, such as tension headaches or temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ). Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, or relaxation techniques can be helpful in managing these conditions.
Making dietary changes: For patients with acid reflux or other gastrointestinal conditions, making dietary changes such as avoiding spicy or fatty foods, reducing portion sizes, or eating smaller, more frequent meals can help to reduce symptoms.
Avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke: Smoking can exacerbate many ENT conditions and is a known risk factor for developing certain types of cancer. Avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke can help to reduce the risk of developing these conditions.
Maintaining proper hydration: Drinking plenty of water and avoiding alcohol or caffeinated beverages can help to reduce the risk of developing dehydration, which can contribute to many ENT conditions.
Using proper hearing protection: For individuals who are regularly exposed to loud noises, using proper hearing protection such as earplugs or noise-cancelling headphones can help to reduce the risk of developing hearing loss or tinnitus.
It’s important to discuss any lifestyle modifications with an ENT specialist in Chennai to ensure that they are appropriate and effective for the individual’s specific condition and needs.
When to visit ENT Doctors
- Hearing Loss: Consult an ENT doctor if experiencing hearing difficulties.
- Sinus Issues: Persistent sinus infections or congestion warrant evaluation.
- Throat Pain: Chronic sore throat or discomfort may indicate underlying issues.
- Dizziness or Balance Problems: Seek help for recurring dizziness or balance issues.
- Tinnitus: Persistent ringing or noise in the ears should be examined.
- Nasal Allergies: Chronic nasal allergy symptoms require professional assessment.
- Speech or Swallowing Issues: Difficulty speaking or swallowing necessitates consultation.
- Chronic Cough: Persistent coughing may indicate respiratory or throat problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Chennai boasts a wealth of highly qualified and experienced ENT specialists who are dedicated to providing top-notch care for patients with ear, nose, and throat conditions. Whether you’re seeking treatment for common issues like sinusitis or require specialized care for complex ENT disorders, you can find a range of expertise in Chennai’s medical community. With advanced diagnostic tools, state-of-the-art facilities, and a commitment to patient well-being, Chennai’s ENT specialists continue to offer exemplary services, ensuring the health and comfort of their patients.