Dexa Scan
Overview
Purpose
Preparation
Procedure
Results
Follow-Up
Bone density scanning also known as bone densitometry or dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), is an enhanced form of X-ray technology that is used as a non-invasive bone density test to measure bone loss. It is used to determine body composition because it can aid in measuring the percentage of the body’s lean muscle and fat. The most common purpose of a DEXA scan in Chennai is to evaluate if a person’s bones are weak, about to fracture, or if they have osteoporosis.
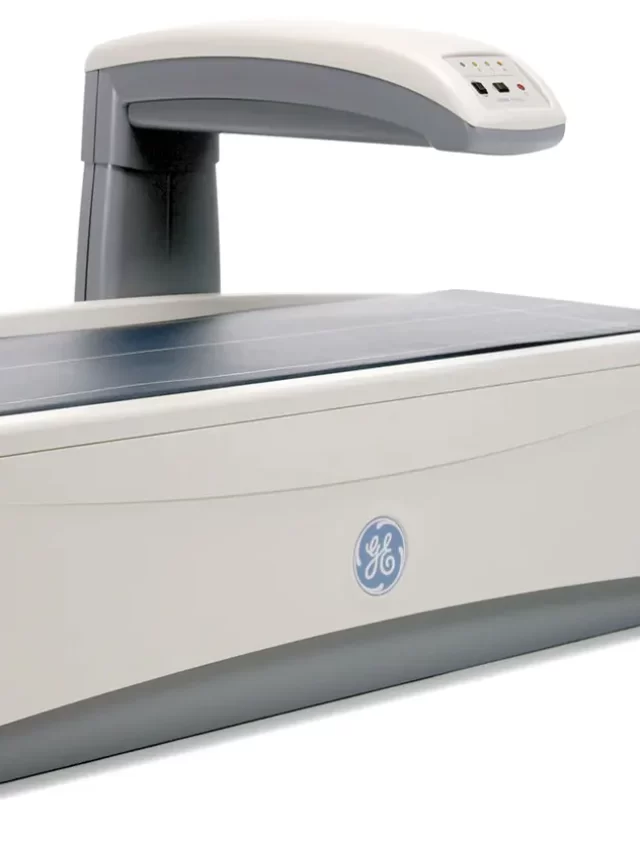
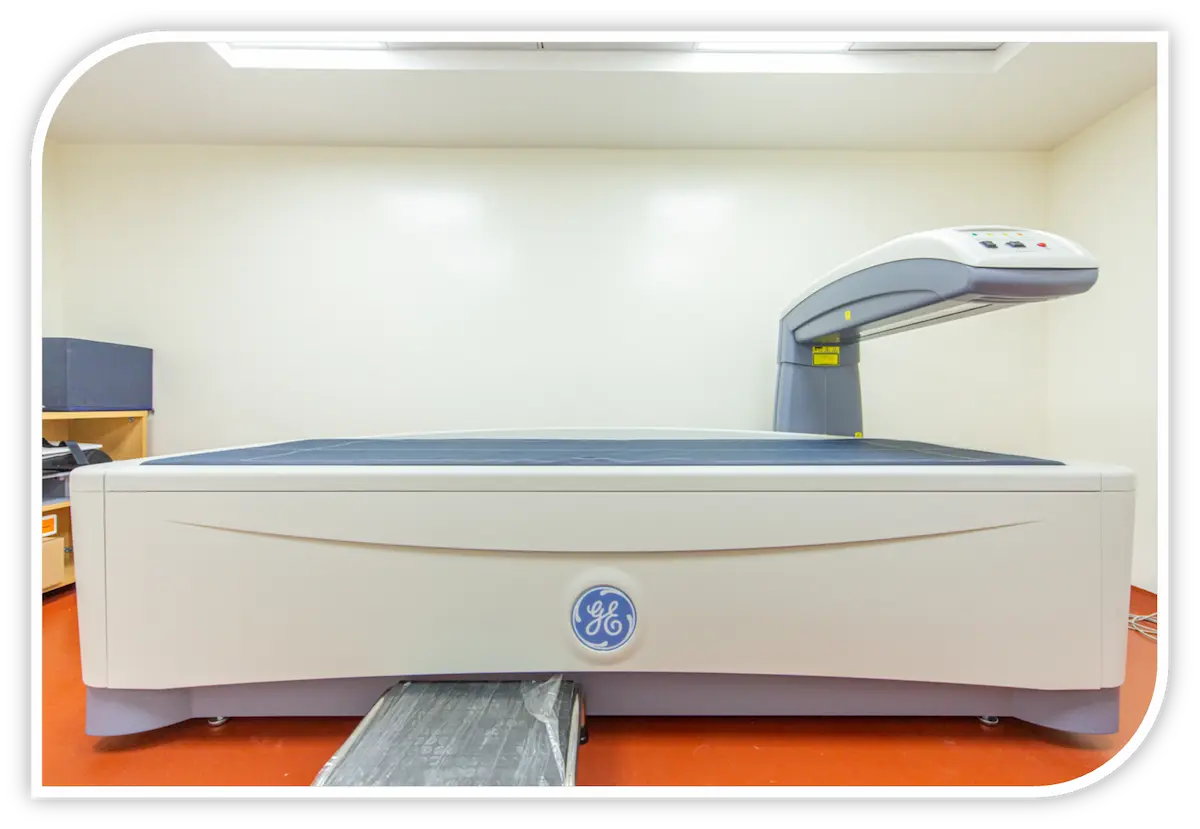
When determining if any patient has a low bone density or if the condition gets worsened, a DEXA scan is considered to be more accurate. Unlike an ordinary X-ray, it can spot even minor changes in bone loss. At Vinita Hospital, a DEXA scan is most often performed on the hips and the lower spine whereby low-energy X-rays are directed through the bone for measuring its mineral density.
An accurate predictor of bone strength is mineral density. The results of this test are used for diagnosing osteoporosis besides assessing an individual’s risk for developing fractures.
Usually, a DEXA scan in Chennai is performed to find weak or fragile bones to assist the probability of a future fracture. In some cases, a DEXA scan evaluates whether someone should take medicine for decreasing bone loss (such as bisphosphonate).

These tests can assess, diagnose & predict the bone strength of a patient. Followed by an initial DEXA scan, follow-up scans will be performed to examine the trajectory of bone loss. The DEXA scan cost in Chennai at Vinita Hospital is reasonable but it varies depending on the body area to be scanned.
Preparation of Dexa Scan in Chennai
DEXA scans are outpatient procedures. There aren’t any special preparations needed for taking the DEXA scan in Chennai except for avoiding the intake of any calcium supplements for 24 hours prior to the test being performed.
The patient have to wear comfortable clothing. Depending on the body area that has to be scanned, the specialist will ask the patient to take off any clothes with zippers, metal fasteners, or hooks. A hospital gown will be provided to wear during the exam.
It is also important to inform the doctor if you have had a CT scan or a barium exam because they may ask you to wait for a few days before scheduling a DEXA scan. Also, the patient should inform the doctor, if they are pregnant or suspect they might be pregnant.
Because the healthcare provider may want to deter the DEXA scan until after the baby gets delivered or might instruct to take special precautions.
The DEXA apparatus consists of a flat padded table that a patient has to lie on. A movable arm above will hold the X-ray detector. A device that produces X-rays will be below the table. The technician will position the patient on the table and may place a wedge under the patient’s knees to help flatten the spine for the image or may position the hip or arm for scanning.
The technician will ask the patient to hold very still when the imaging arm above slowly moves across the body. A vertebral fracture evaluation might also be conducted during a DEXA scan in Chennai to determine if there is any vertebral fracture risk.
The results of a bone density DEXA scan in Chennai make use of a system called a T-score. It is the standard deviation between the measured bone loss and the average.
- A T-score of -1.0 or higher is where the bone density is considered to be normal.
- A T-score of -1.1 to -2.4 is considered osteopenia which means the bone density is low and there can be an increased risk for fracture.
- A T-score of -2.5 or below means osteoporosis exists or there is a high risk for fracture.
A DEXA scan also uses the Z-score to determine the amount of bone a patient has by comparing it with other people belonging to the same size, age, and sex. Here, Z-score above -2.0 is normal, and a score below -2.0 is considered below the normal range.
Our team of medical experts at Vinita Hospital provides excellent facilities and state-of-the-art technology emphasizing precision & reliability. We provide a comprehensive DEXA Scan with an affordable DEXA scan cost in Chennai and ensure that our patients get clarity on the results.
Moreover, the patient will not be required to take the DEXA scan in Chennai for at least two years. However, if the healthcare provider observes that the patient might lose bone rapidly, the patient will be asked to get retested sooner.
Overview
Purpose
Preparation
Procedure
Results
Follow-Up
Frequently Asked Questions
A DEXA (Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry) scan is a medical imaging test that uses low-dose X-rays to measure bone mineral density and body composition. It is a safe and painless test that can help diagnose osteoporosis, a condition in which bones become weak and brittle. A DEXA scan can also help assess the risk of fractures and monitor the effects of treatment for osteoporosis.
A DEXA scan is a simple and non-invasive test that is usually performed on an outpatient basis. Here is how the procedure typically goes:
- You will be asked to lie down on a table, usually face-up, and remain still during the scan.
- The technician will position the DEXA scanner over the area of your body to be scanned. The most common areas scanned are the spine, hip, or wrist.
No, a DEXA (Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry) scan is a painless and non-invasive procedure. During the scan, you will lie on a table while the DEXA scanner passes a low-dose X-ray beam over your body. You will not feel any pain, and there is no need for anesthesia or any other kind of pain relief.
While DEXA (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry) scans are widely used and considered safe, there are a few disadvantages associated with this imaging technique:
-
Radiation Exposure: DEXA scans use a small amount of ionizing radiation, though significantly less than a conventional X-ray. However, individuals who are repeatedly exposed to radiation through multiple DEXA scans over time may face a slightly increased risk of radiation-related complications.
-
Limited Evaluation: DEXA scans primarily focus on assessing bone mineral density (BMD) and are most commonly used for diagnosing and monitoring osteoporosis.
-
Cost and Availability: DEXA scans require specialized equipment and trained technicians to perform and interpret the results. This can make them relatively expensive compared to other diagnostic tests.
-
Limitations for Certain Populations: DEXA scans may be less accurate in certain populations, such as individuals with significantly different body compositions (e.g., obese or heavily muscled individuals) or those with orthopedic implants, which can interfere with the accuracy of the scan results.
-
Lack of Functional Information: DEXA scans primarily focus on bone density and do not provide functional information about the bones or joints.
Yes, DEXA (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry) scans are generally considered safe. The radiation exposure associated with a DEXA scan is very low, significantly lower than conventional X-rays or CT scans. The amount of radiation used in a DEXA scan is generally equivalent to or even less than the radiation exposure from natural sources that we encounter in our daily lives.