Asthma, a persistent respiratory ailment, impacts millions of individuals across the globe. While it can develop at any age, it often starts in childhood and may persist into adulthood. Early detection of asthma symptoms is crucial for effective management and improved quality of life. In this blog post, we’ll explore the key early asthma symptoms to look out for and why it’s essential not to ignore them.
Recognizing Early Asthma Symptoms
Recognizing early asthma symptoms is vital for timely intervention and effective asthma management. This article explores common asthma symptoms and treatment options to help you breathe easier.
Persistent Cough
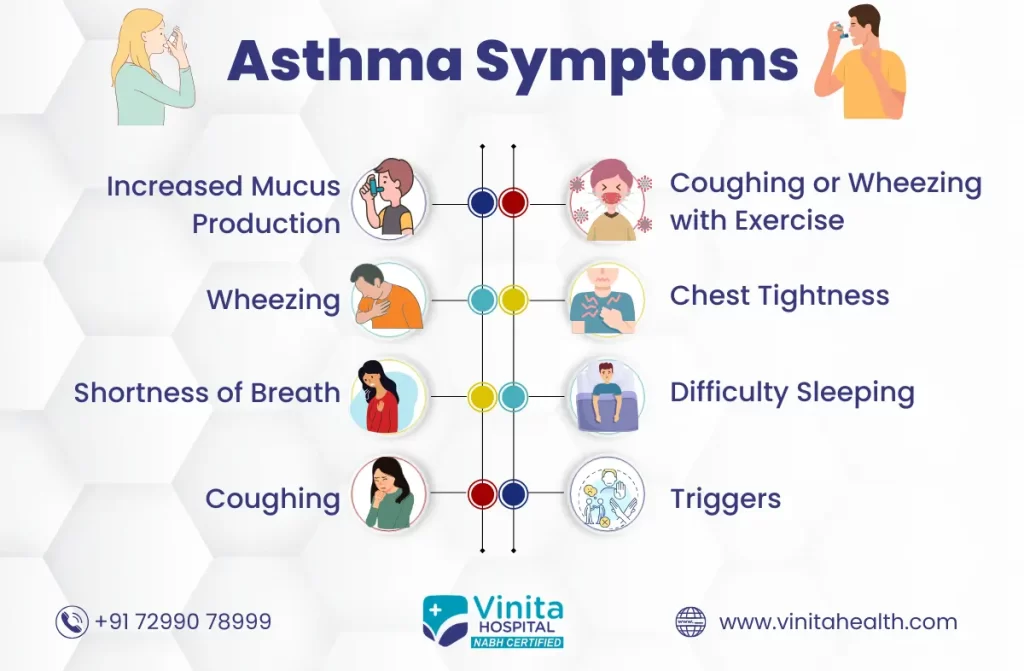
When it comes to recognizing early asthma symptoms, a persistent cough often takes center stage. This symptom is not only one of the earliest indicators but also one of the most prevalent in asthma sufferers. You might notice a persistent, dry, and nagging cough, especially during the night or in the early morning. This cough might initially be dismissed as a common cold or an irritation, but when it lingers for more than a few weeks without an apparent cause, it’s crucial to consider the possibility of asthma.
Asthma-related coughing can be particularly bothersome and disruptive to daily life. It often occurs due to the inflammation and narrowing of the airways, making it difficult for air to pass through freely. This can trigger the cough reflex as the body attempts to clear the airways of any irritants or mucus buildup.
Shortness of Breath
In the realm of early asthma symptoms, shortness of breath is a critical indicator that demands our attention. This symptom, known as dyspnea in medical terms, can manifest as a persistent feeling of breathlessness, making it challenging to catch one’s breath. It often occurs, particularly during physical activities or when exposed to common asthma triggers such as allergens or smoke.
This sensation of breathlessness can be distressing, even frightening, as it can feel like the air is not reaching your lungs as it should. For many individuals, especially those unfamiliar with asthma, this symptom can be perplexing and cause anxiety. It’s important to understand that early detection and intervention are vital to effectively manage asthma.
Wheezing
In the realm of early asthma symptoms, wheezing is a distinctive and often unmistakable sign that warrants careful attention. Wheezing manifests as a high-pitched, whistling, or rattling sound when breathing. This sound is a clear indication that something is amiss within the airways, and it typically occurs when these passages narrow due to inflammation, which is a hallmark of asthma.
Wheezing is a unique asthma symptom as it can occur during both inhalation and exhalation, though it is often more noticeable during exhalation. The sound is produced when the airflow through the narrowed airways encounters resistance, causing vibrations in the surrounding tissues. These vibrations generate the characteristic wheezing sound that is often described as similar to the whistling of the wind.
Chest Tightness
Among the array of early asthma symptoms, the sensation of chest tightness is a particularly distressing and uncomfortable one. Individuals experiencing early stages of asthma may describe this feeling as a noticeable tightness or pressure in the chest area. It’s crucial to recognize that this discomfort is not to be taken lightly, as it can be a telltale sign of underlying asthma.
Chest tightness in asthma is closely linked to the inflammation and constriction of the airways. As the air passages become inflamed, they narrow, restricting the flow of air in and out of the lungs. This constriction creates a sense of tightness or pressure in the chest, which can be especially pronounced during asthma episodes or when exposed to asthma triggers.
Increased Mucus Production
One of the lesser-known but significant early asthma symptoms is the increased production of mucus in the airways. While many people may not immediately associate excess mucus with asthma, it plays a pivotal role in the condition. Understanding this symptom is crucial for early detection and effective management.
Asthma can trigger an overproduction of mucus within the respiratory system. This excessive mucus production serves as the body’s defense mechanism to trap and remove irritants, such as allergens or pathogens, from the airways. However, in individuals with asthma, this response becomes exaggerated and chronic, leading to persistent congestion and coughing.
Difficulty Sleeping
Among the early asthma symptoms, difficulty sleeping is a particularly challenging and disruptive manifestation of the condition. Asthma symptoms often tend to worsen at night, leading to disrupted sleep patterns and potentially impacting overall well-being.
Many individuals with asthma, especially those in the early stages of the condition, find that their symptoms become more pronounced during the nighttime hours. This nocturnal worsening of symptoms can include coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and increased mucus production. These symptoms can significantly interfere with the ability to fall asleep and stay asleep, resulting in poor sleep quality.
Allergies and Allergic Reactions
In the complex web of early asthma symptoms, the presence of allergies and allergic reactions plays a pivotal role. There is a strong connection between asthma and allergies, and understanding this relationship is crucial for early detection and effective management.
A significant number of individuals with asthma also have allergies, a condition known as allergic asthma. Allergens, which are substances that trigger allergic reactions, can be potent asthma triggers as well.
Asthma Treatment
1. Medications: There are two main categories of asthma medications used in asthma symptoms and treatment:
- Controller Medications (Long-term): These are taken regularly to control asthma symptoms and reduce airway inflammation. Examples include inhaled corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers, long-acting beta-agonists, and biologics.
- Reliever Medications (Short-term): These are used for quick relief of acute symptoms and to relax the airways during an asthma attack. Short-acting beta-agonists (e.g., albuterol) are commonly used as rescue inhalers.
2. Inhalers: Most asthma medications are delivered through inhalers, which allow the medication to reach the airways directly.
3. Nebulizers: In some cases, particularly for young children or individuals with severe asthma, a nebulizer may be used to deliver medication as a mist that can be inhaled.
4. Allergen and Trigger Management: Identifying and avoiding asthma triggers is an important part of managing asthma symptoms and treatment. This may involve making changes to your environment, such as using air purifiers, reducing exposure to allergens, and quitting smoking.
Conclusion
Early detection and management of asthma are critical for maintaining a good quality of life. If you or a loved one experiences any of these early asthma symptoms, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. Asthma is a manageable condition, and with the right treatment plan, you can live a full and active life. Remember that asthma symptoms can vary from person to person, so it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment. By being proactive, you can take control of your asthma and breathe easier.
Read also Early Symptoms of Hernia.






