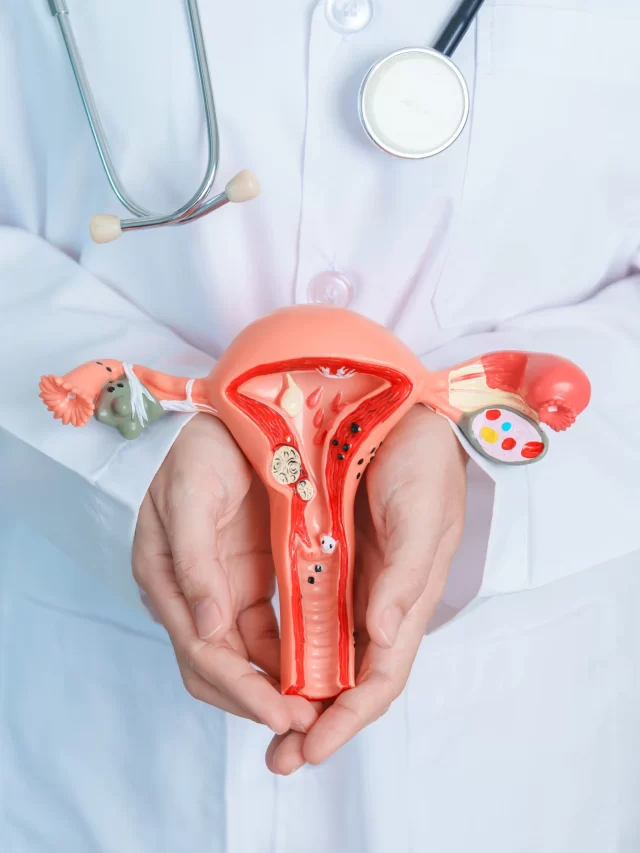
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex hormonal disorder that affects many individuals, primarily those in their reproductive years. Characterized by a range of the most common symptoms of PCOS, it can have a significant impact on physical health, emotional well-being, and fertility.
Overview of Most Common Symptoms of PCOS
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a prevalent endocrine disorder that affects individuals with ovaries, typically during their reproductive years. The syndrome’s name, “polycystic,” can be misleading, as not all individuals with PCOS develop cysts. Instead, it is marked by a constellation of the most common symptoms of PCOS resulting from hormonal imbalances.
Irregular Menstrual Cycles
One of the hallmark PCOS symptoms during pregnancy is irregular menstrual cycles. Menstrual irregularities can manifest as infrequent, prolonged, or absent periods. This occurs due to disrupted hormonal signaling, particularly involving insulin and androgens (male hormones). High levels of androgens can hinder the development and release of eggs, leading to irregular ovulation.

Check out IUI Treatment in Chennai.
Ovulatory Dysfunction
PCOS often leads to anovulation, where eggs are not released regularly from the ovaries. This can contribute to infertility, as ovulation is essential for conception. The most common symptoms of PCOS like hormonal imbalances disrupt the intricate hormonal cascade required for ovulation to occur.
Hyperandrogenism
Elevated levels of androgens such as testosterone are a common feature of PCOS. This can lead to various effects of PCOS on pregnancy including excess facial and body hair (hirsutism), acne, and male-pattern baldness (alopecia). Androgen excess can stem from ovarian and adrenal sources and contributes to the development of other PCOS symptoms.
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is often present in individuals with PCOS. This condition impairs the body’s ability to utilize insulin efficiently, leading to increased insulin production. High insulin levels contribute to androgen overproduction and further exacerbate hormonal imbalances. Insulin resistance that falls under the most common symptoms of PCOS is also associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
Weight Fluctuations and Obesity
Weight gain and obesity are prevalent among individuals with PCOS. Excess adipose tissue contributes to insulin resistance, which can worsen hormonal imbalances. Conversely, the effects of PCOS on pregnancy like hormonal imbalances can promote weight gain, creating a vicious cycle. Weight management strategies, including dietary modifications and regular exercise, play a crucial role in PCOS management.
Skin Issues
PCOS often manifests as skin problems. Alongside acne and hirsutism, individuals may experience the most common symptoms of PCOS like skin darkening (acanthosis nigricans) in body folds, such as the neck and armpits. This hyperpigmentation is linked to insulin resistance.
Mood Disorders
Emotional well-being can be compromised in individuals with PCOS. Hormonal fluctuations, body image concerns, and the psychological impact of dealing with PCOS symptoms during pregnancy can contribute to mood disorders, including anxiety and depression.
Fertility Challenges
The combination of irregular ovulation and hormonal imbalances can make conception difficult for individuals with PCOS. Reproductive technologies, such as ovulation induction and In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), are often used to assist in overcoming the most common symptoms of PCOS besides achieving pregnancy.
Metabolic Complications
Insulin resistance and obesity increase the risk of metabolic complications among individuals with PCOS. These complications include type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. Regular medical monitoring and lifestyle modifications are crucial in managing these PCOS symptoms during pregnancy.
Long-Term Health Implications
PCOS is not limited to reproductive years; its effects can extend into later life. Women with a history of PCOS have increased effects of PCOS on pregnancy like cardiovascular disease, endometrial hyperplasia, and certain cancers. Long-term health management should encompass both reproductive and non-reproductive health concerns.
Conclusion
To conclude, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome presents a wide array of symptoms that can significantly impact the lives of affected individuals. If you suspect you have PCOS or are experiencing any of these the most common symptoms of PCOS, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional at Vinita Hospital for accurate diagnosis and personalized management strategies.
Read also Infertility Specialist in Chennai.