Diabetes is one of the most widespread diseases and it is even recognized to be a global pandemic. A good thing about this epidemic is that if you diagnose it early, you can keep it at bay and not let it affect your daily life. This article will tell you how diabetes can affect different parts of your body and how to look out for it.
Why do you get diabetes? (Diabetes and its effects on your body)
Glucose is the main source of energy and insulin (a compound produced by the pancreas) is what transports it throughout the body. When the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin, some glucose ends up being stagnant in blood, never making it to the organs. This is when you observe high blood sugar and when it crosses the healthy levels (over 126 mg/dL in fasting), it is diabetes.
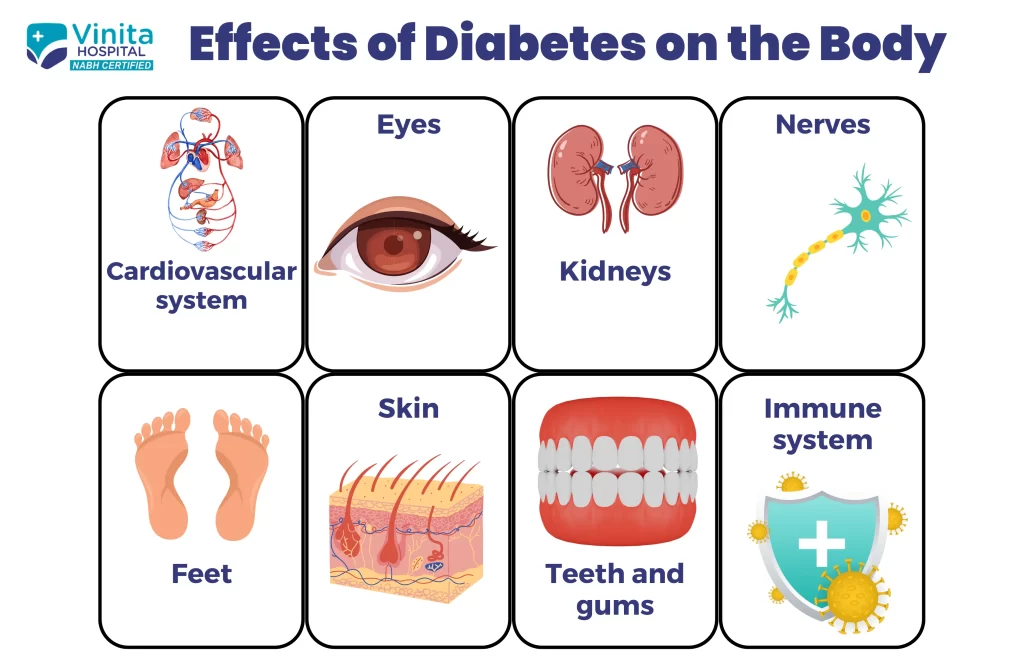
Effects of diabetes on your body
Heart
Diabetes can increase the risk of heart diseases by affecting nerves and blood vessels. If the blood pressure is also high, constant monitoring and a shift to a healthy lifestyle are required. It is advised that you take tests annually or twice a year to check your blood sugar levels, cholesterol, and blood pressure.
Nerves
Diabetes can cause the hardening of blood vessels due to which blood circulation can get affected. It is also called diabetic neuropathy and it mostly affects your feet and legs. If left unnoticed, it can cause serious health issues.
Consult a doctor immediately if a cut or sore on your foot takes long to heal or is getting infected. Other symptoms to watch out for are sensations like burning, pain, or weakness in your limbs that affect your daily life, dizziness, or changes in digestion, urination, or sexual function.
Kidneys
As the blood purifier of the body, diabetes can have harmful effects on the kidneys. When a person has diabetes, the kidneys have to work harder than usual to purify the blood. Over time, they wear out and the blood cells in it get damaged, narrowed, and clogged. This is called diabetic nephropathy. If not taken care of properly, it can lead to the loss of kidney function.
If you are looking for a diabetologist near you who can provide treatment for nephropathy, come to Vinita Hospital. Especially if you have the following symptoms:
- Swelling in feet, ankles, hands, or eyes
- Increased need to urinate
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Confusion or difficulty while concentrating
- Persistent itching, nausea, or vomiting.
This is not an exhaustive list of symptoms and you might not see any symptoms at all at the early stages. Many identify it through periodical check-up only.
Skin
Sometimes one might experience skin conditions due to diabetes and it is called diabetic dermopathy. It is not an alarming condition of diabetes yet it should be given attention as it directly reflects the level of blood sugar. Watch out for symptoms like pigmented patches on the skin that are itchy or painful, dark areas on the skin that feels like velvet, hard or thickening skin, blisters, and the outbreak of small bumps.
Eyes
If diabetes is left unmanaged, it can affect one’s eye. While the early symptoms include blurriness, dark areas of vision, difficulty identifying colors, and floaters, it can lead to blindness. But as long as you manage your diabetes well, you needn’t be worried.
As you can see, the majority of health issues that occur because of diabetes can be prevented or controlled through proper diabetes management. The first step in the treatment of diabetic patients is the diagnosis and constant monitoring of the blood sugar level. Reading about diabetes on the internet can be overwhelming as there is too much information and not everything will apply to you.
Get proper diabetes care from diabetes screening to diabetes management at Vinita Hospital. If you are looking for the best diabetes hospital in Chennai, come to Vinita Hospital for healthcare that is trusted by patients.